Mar 2020
It is not that long ago, we just have shifted from room-sized computers to smart devices and powerful computers that can fit in the palm of our hands. We are in the digital revolution era, in which technology is accelerating at exponential speed and today robotic process automation (RPA) is one of those revolutionary technologies.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
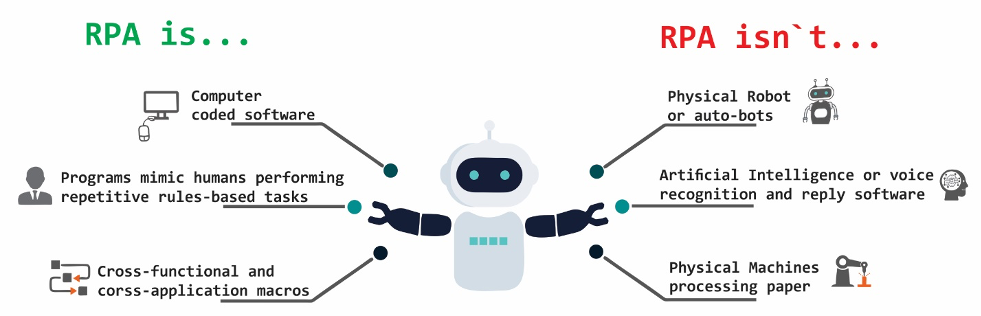
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software, commonly known as a ‘robot’, to automate and standardize repeatable business processes, in a very simplified way. We can think of RPA as a digital robot that can mimic the routine or predictable processes of a human on a computer.
More time for strategic work
What makes RPA unique is its ability to mimic human work faster and continuous operation without errors.
With little to no manual intervention RPA, “robots” will perform repetitive, time-consuming, regulated tasks of human workers without fatigue for 24 hours such as data entry, customer service queries, data extraction and process standard transactions. This allows employees to focus on and spend their time and energy on strategic higher-level work instead of routine tasks.
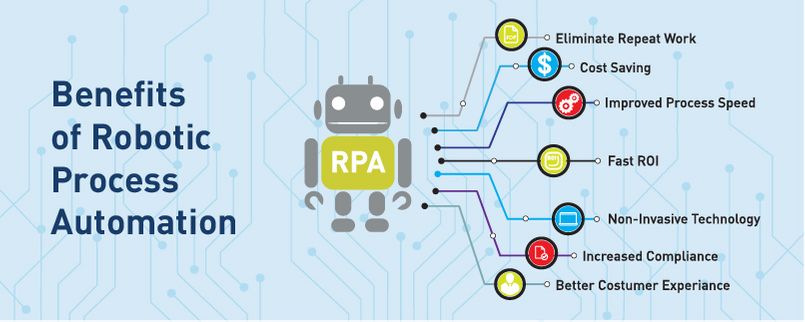
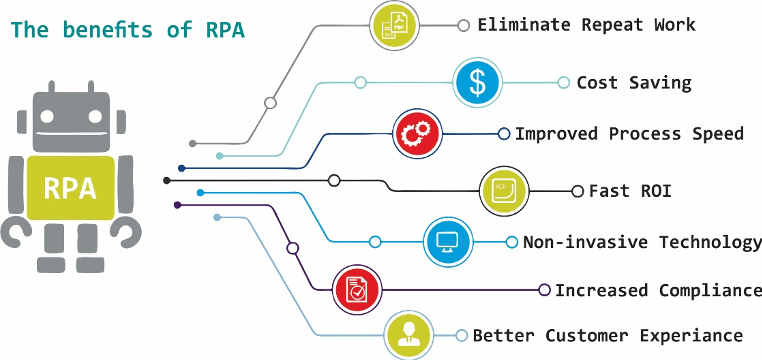
Benefits of RPA
RPA implementation is not that much costly compared with other automation technologies and can rapidly return financial and nonfinancial benefits that affect the most common performance measures
It is like a virtual employee that runs 24/7, based on computation resources assigned to them or triggers. RPA will improve the productivity, eliminate the risks of human errors and work delays, provide high productivity and digitize existing business processes.
Due to the various benefits of RPA, its utilization is gradually increasing in the market globally. Most of the companies are already implementing RPA technology, as it cuts the cost and frees the other resources.
Regardless of the technology used in the infrastructure or the repetitive work handling process, adopting a RPA solution into business process should be carried out via a well-defined governance structure and requires proper process evaluation & selection methods.
Use Cases
Based on our implementation experiences Human Resources, Purchasing, Accounting, Financing, Information Technologies and Treasury processes are most likely to be migrated to RPA. Automating employee recruitment processes, private pension transactions, preparation of financial reports and entering the data to ERP system takes considerably much amount of time. RPA does not only saves time but also improves the efficiency and the quality of the processes to be automated.
